In the machine vision industry, the composition of a machine vision system can be divided into two parts: hardware and software. Among them, the hardware selection of machine vision is also extremely important, and the following is a brief introduction to the precautions for the selection of machine vision light sources, cameras and lenses by Xinxiwang:
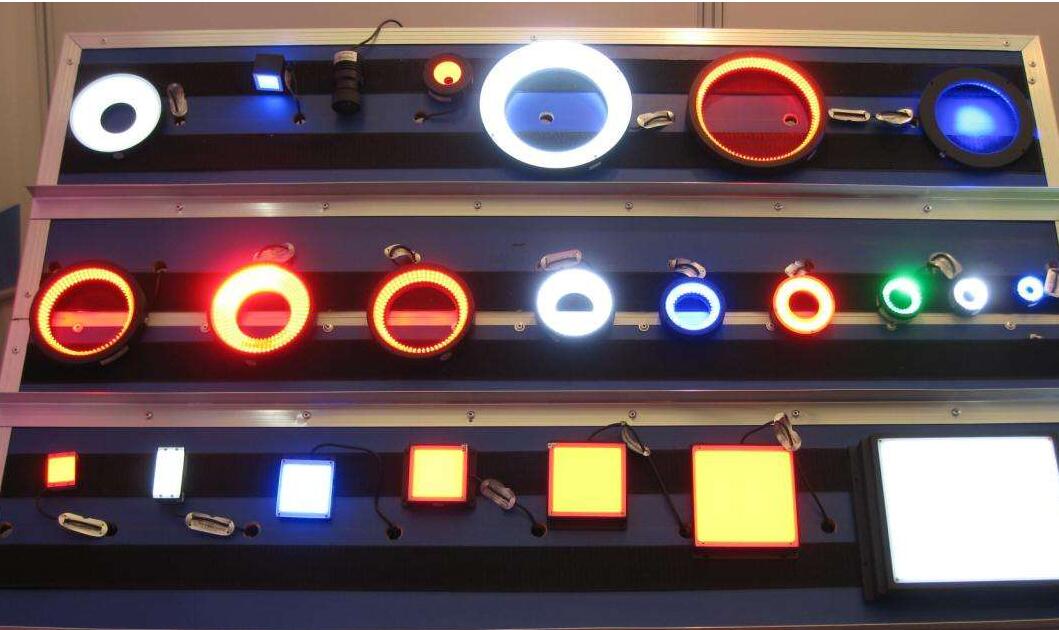
First, the selection of light source
There are two main functions of light sources. First, make the observed features produce the largest contrast between the background and make the features stand out and easy to distinguish; Second, it is to maintain sufficient brightness, eliminate the interference of external light, and ensure the stability of the image.
Consider the following two parties when choosing a light source:
The color of the light source: An object appears a certain color because it reflects the corresponding spectrum. If you want to change a certain color to white when photographing an object, use a light source (with the same or similar wavelength) that is the same or similar to that color; If you want to shoot black, use a light source with a large wavelength difference from the target color.
If the background is blue and the testing equipment is white, you need to shoot the background black, so choose a red-light source. Red LEDs not only have a long lifespan, stable performance, and low price, but more importantly, their wavelengths are closer to the sensor's sensitivity peak.
The shape of the light source: The commonly used light sources for machine vision include ring light source, bar light source, backlight, coaxial light source, etc., considering the convenience of mechanism installation and the need for uniform illumination.

Second, the camera selection
Industrial cameras can be divided into black and white cameras and color cameras according to the imaging color; According to the scanning method, it can be divided into line scan camera and area scan camera; According to the sensor type, it can be divided into CCD camera and CMOS camera.
Camera selection should first determine the following issues according to the project requirements:
Determine the accuracy requirements of the tested product;
Determine the size of the field of view that the camera wants to see;
Determine the velocity of the object to be detected;
Determine whether it is a dynamic or static detection.
The second is to determine the hardware type of the camera, and select the camera data transmission interface: 1394, Gige (Gigabit network), USB, camera link. Then, according to the matching with the lens, select the appropriate camera sensor size (the largest compatible sensor size of the lens is greater than or equal to the sensor size of the camera) and the interface type (C or CS) with the lens.
The error of the vision system hardware is unavoidable, and the error between 1~2 pixels is generally guaranteed, so through the calculation formula: accuracy = field of view (length or width) ÷ camera pixels (length or width). For example, if the field of view is 100×60 and the accuracy is 0.1, considering the hardware error, the accuracy is generally 0.05 when selecting the model, then the pixels on the long side of the camera = 100÷0.05 = 2000, and the pixels on the short side are 60÷0.05 = 1200, so only the camera with a theoretical resolution greater than or equal to 2000×1200 pixels can meet the requirements.
Third, the selection of lenses
Do I need to use a telecentric lens? Telecentric lenses are generally considered for precision dimensional measurements. The main function of the telecentric lens is to correct the parallax of the traditional industrial lens, which can make the image magnification unchanged within a certain object distance.
Telecentric lenses are divided into object telecentric, image telecentric and bilateral telecentric, where optical magnification = camera sensor size / field of view size = sensor (V) or (H) size / field of view (V) or (H), the larger the field of view, the smaller the magnification. In general, telecentric lenses have a fixed focal length and working distance, and some telecentric lenses are large and heavy, so it is necessary to understand the customer's requirements for field size, working distance, space constraints and motion control in detail before determining the lens model that needs to be selected.
Depth of field of the lens: The distance of space from which the camera can image clearly in the vertical direction, which is called depth of field. The shorter the focal length, the greater the depth of field; The smaller the aperture, the greater the depth of field; The farther away the lens is from the object, the greater the depth of field; The larger the pixel of the camera sensor, the greater the depth of field.
The largest compatible chip size of the lens: The largest compatible chip size of the machine vision lens must be greater than or equal to the sensor size of the camera, otherwise it will cause serious distortion and phase difference.
Interface of machine vision lens: Both machine vision lens mount and camera mount are divided into C, CS, F, and other larger size mount types. The camera and lens are matched to each other, that is, the C-mount camera can only use the C-mount lens, and the CS-mount camera can use the CS-mount lens and the C-mount lens with a 5mm bezel.
Focal length of machine vision lens: The selection of lens focal length is based on the formula focal length f=working distance × camera sensor size (HorV)/FOV (HorV) to select the appropriate focal length lens.
Chengdu Xinxiwang Automation Co., Ltd. specializes in the sales of machine vision systems, machine vision light sources, machine vision software, machine vision sensors, industrial cameras, industrial lenses and other products, welcome to inquire!
Phone:028-62705808
Fax:028-62705808
Mobile Phone:18215640190
Email:sales@cdxiwang.com
Address:2-8-6, Chen Electric Technology Innovation Park, 68 Shuangbai Road, High-tech West District, Chengdu