Typically, a PC-based machine vision system can inspect 20-25 parts per second, which is closely related to the number of inspected parts, the processing program, and the speed of the computer.
The eye vision system of industrial robots usually consists of the following:
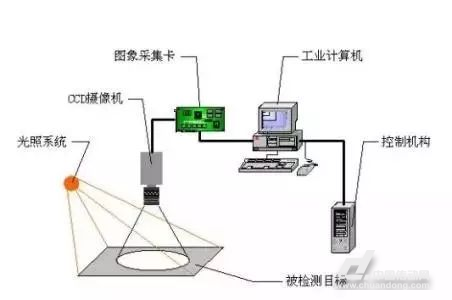
01. Cameras and optical components
This category usually contains one or more cameras and lenses (optical components), which are used to photograph the objects being detected. Depending on the application, cameras can be based on standards such as black and white, composite color (Y/C), RGB color, non-standard black and white (variable scan), progressive-scan or line scan.
02. Lighting
Lighting is used to illuminate parts in order to capture better images from the camera. Lighting systems can be in different shapes, sizes and brightness. Common forms of lighting are high-frequency fluorescent lamps, LEDs, incandescent lamps and quartz-halogen optical fibers.
03. Component sensors
usually appear in the form of gratings or sensors. When this sensor senses the proximity of a component, it gives a trigger signal. This sensor tells the machine vision system to capture an image when the part is in the correct position.
04. The image capture card
is also called a video capture card. This component is usually a card plugged into the PC.
The purpose of this capture card is to connect the camera to the PC. It obtains data (analog signal or digital signal) from the camera and then converts it into information that the PC can process.
It can also provide signals to control camera parameters (such as trigger, exposure time, shutter speed, etc.). There are many forms of image capture cards, supporting different types of cameras and different computer buses.
05. PC platform
computer is a key component of machine vision.
In detection applications, Pentium or higher CPUs are usually used. Generally speaking, the faster the computer, the less time it takes the visual system to process each image.
Since there are often vibrations, dust, heat radiation, etc. in manufacturing sites, industrial-grade computers are generally required.
06. Inspection software
Machine vision software is used to create and execute programs, process the collected image data, and make "PASS/FAIL" decisions.
Machine vision has many forms (C language library, ActiveX control, point-and-click programming environment, etc.), which can be a single function (such as designed only to detect LCD or BGA, alignment tasks, etc.), or it can be multi-functional (such as designing One package that includes metrology, barcode reading, robot navigation, field verification, and more).
07. Digital I/O and network connection
. Once the system completes this detection part, this part must be able to communicate with the outside world. For example, it needs to control the production process and send "PASS/FAIL" information to the database. Usually, a digital I/O board and/or a network card are used to communicate between the machine vision system and external systems and databases.

Careful planning and attention to detail when configuring a PC-based machine vision system can help you ensure that your inspection system meets your application needs. Here are a few points you must consider:
Determine your goals. This is probably the most important step. Decide what you need to achieve in this inspection task. Inspection tasks are usually divided into the following categories:
Measurement or metrology
Reading characters or codes ( barcode) information.
Detection of objects State
recognition and recognition of special characteristics Pattern recognition
Comparison or matching of objects with templates
Machine or robot navigation The detection process can consist of just one operation or contain several tasks related to the detection task.
In order to confirm your mission, you should first identify the tests you need to do to maximize the inspection of the component, that is, you can take into account the defects that will occur.
In order to clarify what is most important, it is best to make an evaluation sheet and list the "must do" and "can do" tests. Once the principal is satisfied with the test criteria, more tests can then be added to improve the inspection process. It is important to remember that adding tests also increases the inspection time.
Determine the speed you need – how long does it take for the system to inspect each component?
This is not only determined by the speed of the PC, but also by the speed of the production line.
Many machine vision systems include clocks/timers, so the time required for each step of the inspection operation can be accurately measured. From this data, we can modify our programs to meet timing requirements. Typically, a PC-based machine vision system can inspect 20-25 parts per second, which is closely related to the number of inspected parts, the processing program, and the speed of the computer.
Choose Your Hardware Smartly
The performance of a machine vision system is closely related to its components. In the selection process, there are many shortcuts, especially in optical imaging, which may greatly reduce the efficiency of the system. The following are a few basic principles that you must keep in mind when selecting components:
01. Camera The choice of camera is directly related to the needs of the application. Three points are usually considered:
a) black and white or color;
b) movement of the component/target;
c) Image Resolution.
Black and white cameras are mostly used in inspection applications because black and white images provide 90% of the visible data and are cheaper than color. Color cameras are mainly used in situations where color images need to be analyzed. Depending on whether the part moves during inspection determines whether we choose a standard interlaced camera or a progressive scan camera. In addition, the image resolution must be high enough to provide sufficient data for the detection task. Finally, the camera must be of good quality and immune to vibration, dust and heat found in industrial sites.
02. The crucial factors of optical components and lighting are often ignored.
When you use poor optics or lighting, even if you use the best machine vision system, it will not perform as well as a lower-capacity system with good optics and proper lighting. The goal of the optics is to produce the best and largest image available area and to provide the best image resolution. The goal of illumination is to illuminate key features of the part that needs to be measured or inspected. Typically, the design of a lighting system is determined by factors such as: color, texture, size, shape, reflectivity, etc.
03. Image capture card Although the image capture card is only a component of the complete machine vision system, it plays a very important role.
The image grabber directly determines the camera interface: black and white, color, analog, digital, etc.
Using an analog input frame grabber, the goal is to convert the image captured by the camera into digital data as unchanged as possible. Using an incorrect frame grabber may result in erroneous data.
Industrial frame grabbers are usually used for inspection tasks. Multimedia grabbers are not used in this field because they change the image data through automatic gain control, edge enhancement and color enhancement circuits. The purpose of the image capture card using digital input is to convert the digital image data output by the camera and send it to the PC for processing.
01. Consider various variations:
Human eyes and brains can identify targets under different conditions, but machine vision systems are not so versatile and can only work according to programmed tasks. Knowing what your system can and cannot see can help you avoid failures (such as mistaking good parts for bad) or other detection errors. General considerations include part color, ambient light, focus, part position and orientation, and large changes in background color.
02. Choose the right software:
Machine vision software is the intelligent part of the inspection system and the core part. The choice of software determines the time it takes you to write the debugging detection program, the performance of the detection operation, and so on.
Machine vision provides a graphical programming interface (often called "Point & Click") that is generally easier than other programming languages (such as Visual C++), but has certain limitations when you need some special features or functionality. Code-based software packages, although very difficult and require coding experience, provide greater flexibility in writing complex application-specific detection algorithms. Some machine vision software provides both graphical and code-based programming environments, providing the best of both worlds and providing a lot of flexibility to meet different application needs.
03. Communicate and record data:
The overall goal of a machine vision system is to achieve quality inspection by distinguishing good and bad parts. In order to achieve this function, the system needs to communicate with the production line so that it can take some action when a bad part is found. Typically these actions are through digital I/O boards that are connected to PLCs in the manufacturing line so that bad parts can be separated from good parts.
For example, machine vision systems can be connected to a network so that data can be transferred to a database, which can be used to record the data and allow quality controllers to analyze why rejects occur. Careful consideration at this step will help seamlessly integrate the machine vision system into the production line. Questions to consider are:
What type of PLC is being used and how is its interface?
What type of signals are required?
What type of network is or must be used?
What is the file format that is sent over the network? Typically the RS-232 port is used Communicate with the database to record data.
Phone:028-62705808
Fax:028-62705808
Mobile Phone:18215640190
Email:sales@cdxiwang.com
Address:2-8-6, Chen Electric Technology Innovation Park, 68 Shuangbai Road, High-tech West District, Chengdu